3DGS
这是在西湖大学实验室做3DGS相关项目的记录,由于但是时间匆忙这是之后整理了的比较混乱。
算法总览

“%ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\Common7\Tools\VsDevCmd.bat”
set http_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:7890
set https_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:7890
COLMAP cameras.bin, images.bin, points3D.bin
Blender 生成的是合成模拟的数据集,通常导出为:
渲染后的 2D 图像(RGB)
可选 深度图 / 法线图 / 完整几何模型(mesh 或 point cloud)
相机参数(位置、焦距、方向等),可能以
.json,.fbx, 或自定义格式导出,供 NeRF 或 3DGS 使用
| 模块文件 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
dataset_readers.py |
注册数据加载方式,识别是 COLMAP 还是 Blender 数据集类型 |
colmap_loader.py |
读取 cameras.bin, images.bin, points3D.bin 文件,构造基础场景信息 |
cameras.py |
格式化相机信息(JSON 输出,训练/渲染用的相机实例等) |
gaussian_model.py |
核心初始化:从点云创建初始 Gaussians,包括位置、协方差、颜色、透明度 |
docker run –gpus all -it -v E:\3DGS\data:/workspace/local_data -v E:\3DGS\outputs:/workspace/local_outputs -v E:\3DGS\taming-3dgs:/workspace/taming-3dgs kfzzzzzz_3dgs_image:latest bash
pip uninstall -y diff-gaussian-rasterization simple-knn
python train.py
-s /workspace/local_data/treehill
-m /workspace/local_outputs/tamingrun5
–mode final_count
–budget 150000
–cams 10
–sh_lower
–ho_iteration 30000
python render.py
–source_path /workspace/local_data/treehill
–model_path /workspace/local_outputs/tamingrun2
–skip_train
–iteration 30000
–eval
python metrics.py -m /workspace/local_outputs/tamingrun1
裁剪空间

透视投影矩阵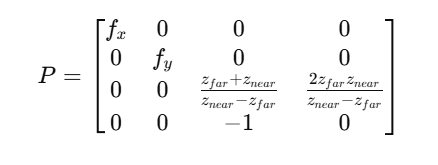
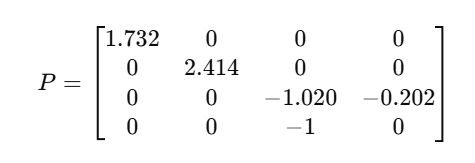
diff_gaussian_rasterization->CudaRasterizer->markVisible->checkFrustum->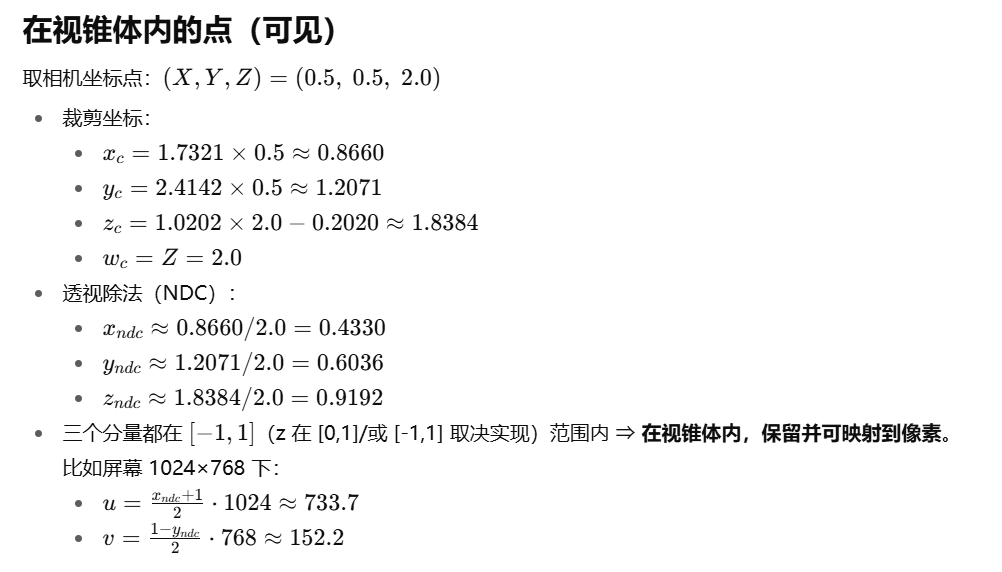

实际只去除了近点(但是在后续 光栅化阶段,如果它们的 footprint 完全不覆盖屏幕,最后的半径 radii=0,PyTorch 侧的 visibility_filter 会把它们排除掉)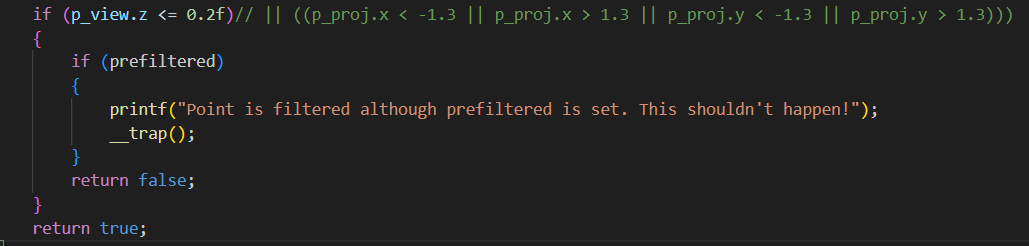
xyz_gradient_accum 累计梯度强度
梯度强度
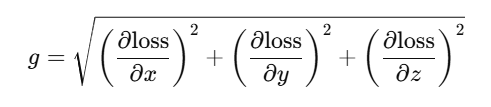

RGB转SH
标准梯度下降



致密化过程
伪代码
1 | if 当前迭代数 < densify_until_iter: # 只在指定范围内做致密化 |
densify_and_prune
1.传入参数
max_grad:梯度阈值。可见点的“累计梯度强度”超过它就认为细节不够,需要加点。min_opacity:不透明度阈值。低于它的点会被视为“几乎透明”,可删。固定0.005extent:场景尺度(如相机包围球半径),用于把“世界尺寸”判断成相对量级。
-self.cameras_extent = scene_info.nerf_normalization[“radius”] ??max_screen_size:屏幕空间半径上限(像素级)。点在屏幕投影太大就删;可能为None。如果透明度还没重置过 阈值为None 重置过 阈值固定20radii:当前这一帧每个点在屏幕上的半径(像素)。
2.计算 累计梯度强度/出现频率
3.densify_and_clone:如果梯度强度对于阈值&&逻辑尺寸小于阈值,直接复制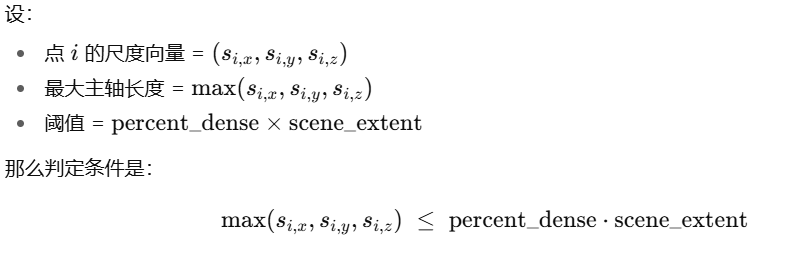
4.densify_and_split:
中心位置偏移:
三轴长度 /0.8*N
5.减枝prune
条件1:self.get_opacity < min_opacity
条件2:big_points_vs = self.max_radii2D > max_screen_size 渲染后半径过大
条件3:big_points_ws = self.get_scaling.max(dim=1).values > 0.1 * extent 轴长过长
透明度重置

self.cameras_extent = scene_info.nerf_normalization[“radius”]
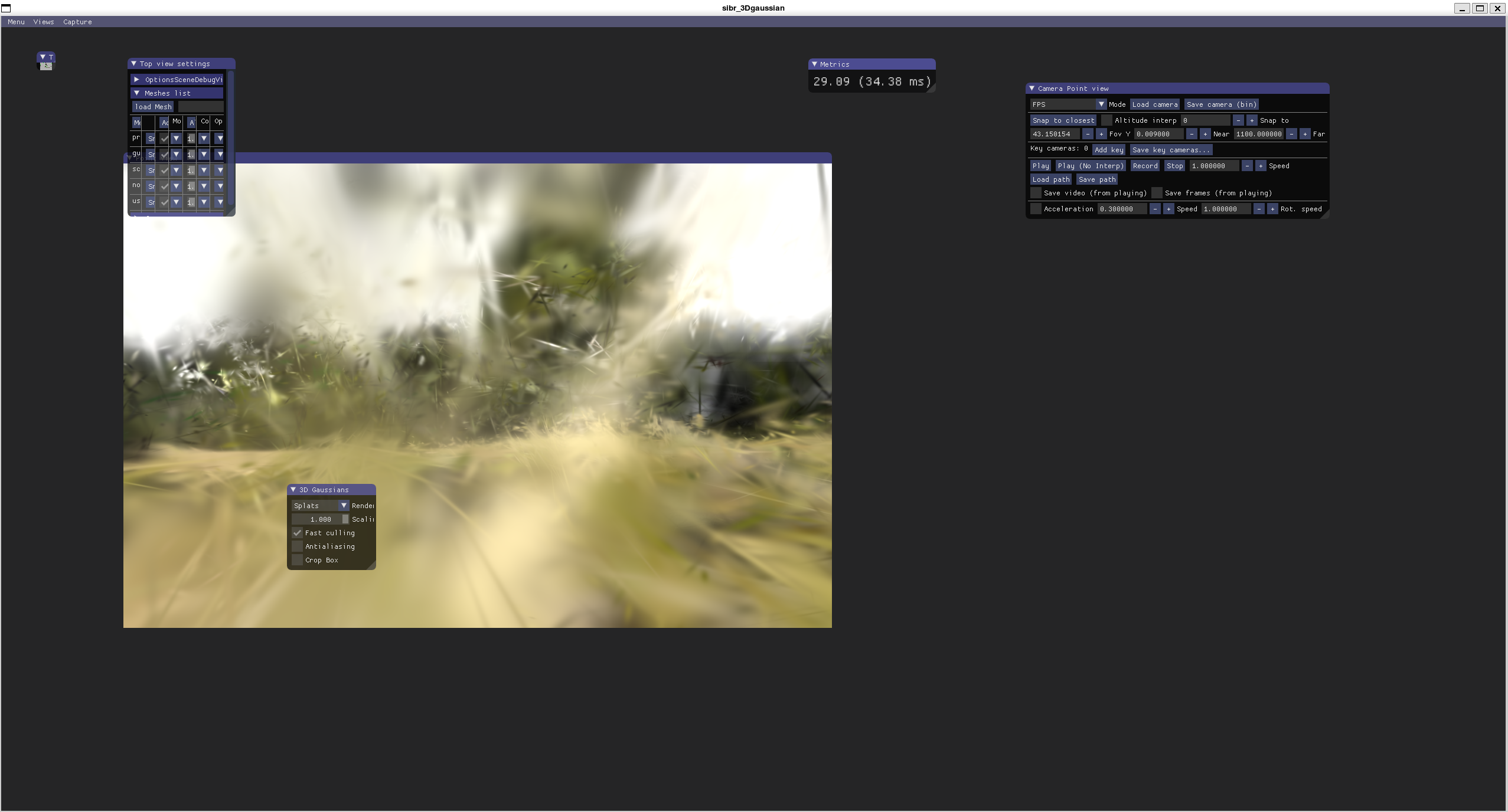
render
输入render参数
render_pkg = render(
viewpoint_cam, # 相机(位姿、内参、分辨率、可选alpha_mask)
gaussians, # 所有高斯体(位置xyz、缩放scaling、旋转、SH特征/颜色、opacity等)
pipe, # 渲染管线配置(光栅化器/着色开关、是否debug等)
bg, # 背景颜色(白或黑或随机RGB)
use_trained_exp=dataset.train_test_exp, # 是否使用已学到的曝光/相机响应修正
separate_sh=SPARSE_ADAM_AVAILABLE # 稀疏Adam可用时,SH参数分离以便只更新“可见点”
)
输入rasterizer参数
means3D:高斯中心 (N×3)means2D:上面那个 screenspace proxyopacity:不透明度- 协方差:
- 如果
pipe.compute_cov3D_python→ 在 Python 端算好cov3D_precomp - 否则交给光栅化器用
scales + rotations计算
- 如果
- 颜色:
- 如果
override_color→ 直接用 - 否则:
pipe.convert_SHs_python→ 在 Python 端用视线方向解码 SH- 否则直接传 SH 系数给光栅化器
- 如果
通过链式法则传递loss到高斯椭球
diff-gaussian-rasterization
1 | function render(viewpoint_cam, gaussians, pipe, bg, use_trained_exp, separate_sh): |
forward
1 | dim3 tile_grid((width + BLOCK_X - 1) / BLOCK_X, (height + BLOCK_Y - 1) / BLOCK_Y, 1); |

forward->preprocessCUDA
半径 边缘触碰置0
近裁剪(见裁剪空间)


排序

render


1 | // Resample using conic matrix (cf. "Surface Splatting" by Zwicker et al., 2001) |

1 | template <uint32_t CHANNELS> |

1 | float val = exp(power); |

1 | float val = exp(power); |

1 | C[ch] += features[collected_id[j] * CHANNELS + ch] * exp(power) * 0.03f; |
![][https://picgo.kfzzzzzz.cn/20250909111643.png]
1 | float val = exp(power); |

1 | C[ch] += features[collected_id[j] * CHANNELS + ch] * val * 0.05f; |
论文阅读
DroneSplat: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Robust 3D Reconstruction from In‑the‑Wild Drone Imagery
会议:(CVPR) 2025
作者:Jiadong Tang, Yu Gao, Dianyi Yang, Liqi Yan, Yufeng Yue, Yi Yang 北理/杭电
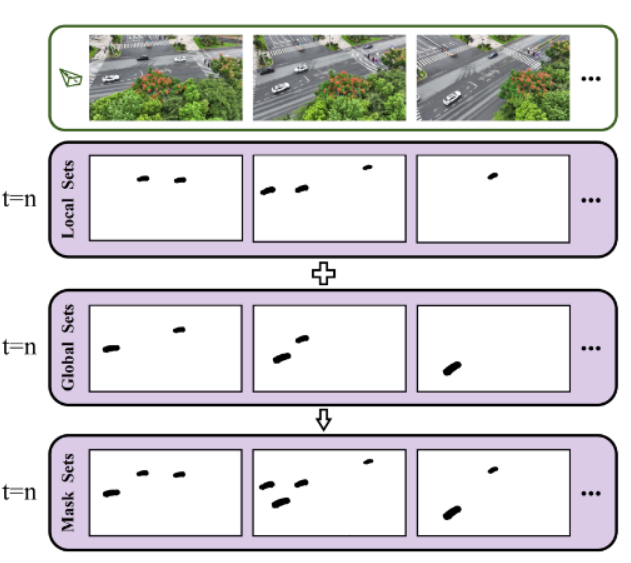
1.自适应局部-全局掩码
思路:
增加mask消除 移动部件对loss影响
![][https://picgo.kfzzzzzz.cn/lunwengongshi1.png]]
1.残差计算(原始loss公式)
![][https://picgo.kfzzzzzz.cn/20251020220809.png]]
2.计算第t次迭代第i个视角第j个对象的残差(每个分割物体的残差)
![][https://picgo.kfzzzzzz.cn/20251020222716.png]
m 由segment anything 分割得到的各个区域
计算局部掩码
3.计算判断移动物体的自适应阈值
计算第t次迭代的残差期望与方差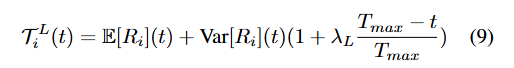
判断所有的移动物体的残差都在残差期望±1个标准差 异常检测阈值:期望+方差
并增加随迭代递减的方差权重项
4.计算mask 部件平均残差超过阈值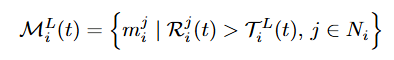
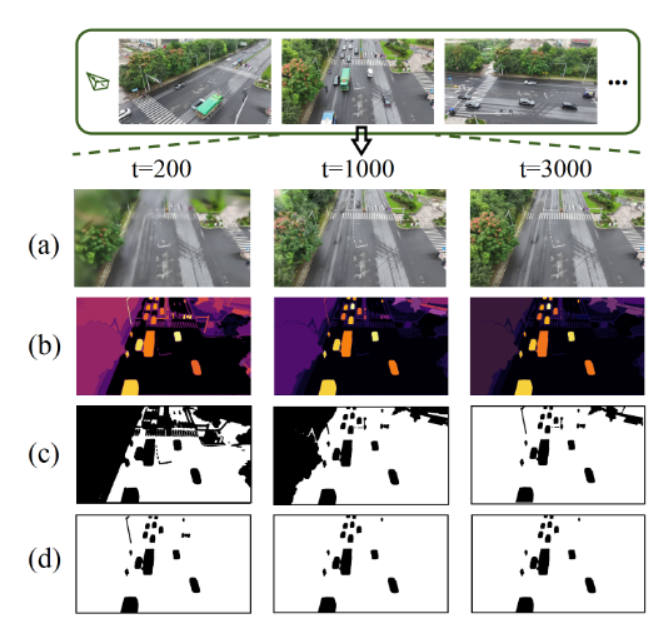
计算全局掩码
5.阈值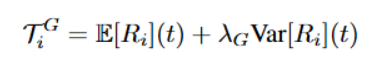
6.某一帧超过阈值的object 提取 中心点和四个边缘点输入 SA 移动mask
7.定义一个全局掩码合集每一次迭代都更新
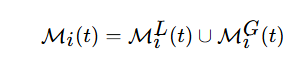
2.Voxel-guided Optimization
1.增加DUSt3R输出稠密点作为几何先验以解决视角稀疏问题
2.筛选点 计算SPFH 并乘上每个点的置信度得到 每个点的score 并选择得分高的点
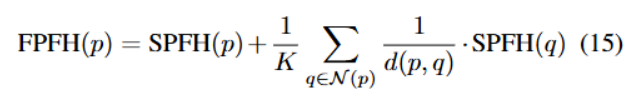
3.划分体素网格,在优化过程中约束高斯点
D2GS: Depth-and-Density Guided Gaussian Splatting for Stable and Accurate Sparse-View Reconstruction
会议:预印本
作者:Meixi Song/Xin Lin/Dizhe Zhang/Haodong Li/Xiangtai Li/Bo Du/Lu Qi Insta360 Research
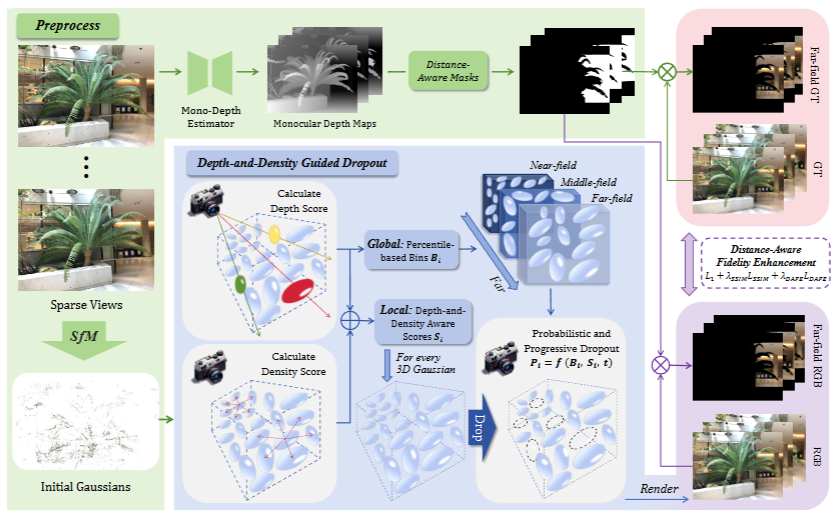
问题:近场过拟合/远场欠拟合
DEPTH-AND-DENSITY GUIDED DROPOUT
1.计算每个高斯的dropout score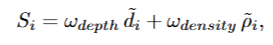
1 | depth_score = (1.0 - (camera_depths - depth_min) / (depth_max - depth_min + 1e-6)).float() |
2.划分近中远三区域,每个区域设置不同的dropout率
1 | near_field = camera_depths <= depth_percentile_33 |
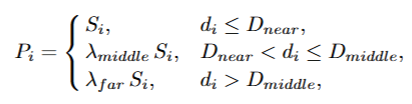
3.增加基于迭代的系数
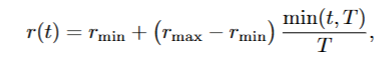
1 | progress = min(1.0, iteration / 10000.0) |
4.最终mask计算
1 | drop_prob = (near_field.float() * combined_score * drop_rate + |
5.实现dropout
1 | opacity = opacity * mask[:, None] |
DISTANCE-AWARE FIDELITY ENHANCEMENT
1.通过单目深度估计模型预测深度图预处理远处1近处0的二值mask(源码中无指出模型,直接是加载preprocess_mask)
1 | far_mask = mask_cache[viewpoint_cam.image_name] |
2.计算distance-enhanced loss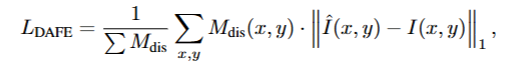
1 | gt_far = apply_mask_to_image(gt_image, far_mask) |
3.加入损失函数
![][https://picgo.kfzzzzzz.cn/20251021010042.png]
INTER-MODEL ROBUSTNESS ASSESSMENT
两个高斯点之间的差异:the Wasserstein distance admits a closed-form via
the Bures metric
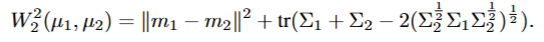
![][https://picgo.kfzzzzzz.cn/20251021013227.png]
计算两个3DGS模型的差异:OT problem over the Gaussian components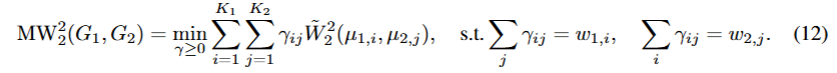
Sinkhorn algorithm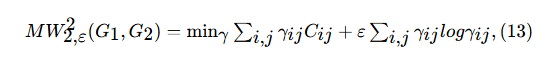
LP‑3DGS: Learning to Prune 3D Gaussian Splatting
会议:NeurIPS 2024
作者:Zhaoliang Zhang, Tianchen Song, Yongjae Lee, Li Yang, Cheng Peng, Rama Chellappa, Deliang Fan
单位:Johns Hopkins University
内容: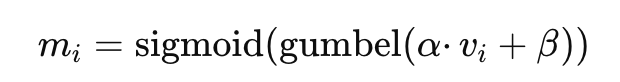
每一次都把这个mask加到opacity上,在训练结束后进行硬剪枝
pixelSplat: 3D Gaussian Splats from Image Pairs for Scalable Generalizable 3D Reconstruction
会议:CVPR 2024
作者:David Charatan, Sizhe Li, Andrea Tagliasacchi, Vincent Sitzmann
单位:MIT/google research
内容:一个前馈模型 “pixelSplat”,从输入一对图像 + 相机参数出发,预测场景的3D 高斯基元表示。网络框架:Two-view Image Encoder+Pixel-aligned Gaussian Prediction
SuGaR: Surface-aligned Gaussian Splatting for Efficient 3D Mesh Reconstruction and High-quality Mesh Rendering
会议 :CVPR 2024
作者: Antoine Guédon、Vincent Lepetit
单位:法国
内容:提出 Surface-aligned regularization 使高斯分布与表面对齐,并通过 Poisson 重建提取三角网格;在此基础上可联合优化高斯与网格,实现可编辑的混合表示,渲染质量高、几何一致性好。
2D Gaussian Splatting for Geometrically Accurate Radiance Fields
会议:SIGGRAPH 2024
作者:Binbin Huang, Zehao Yu, Anpei Chen, Andreas Geiger, Shenghua Gao
单位:上海科技大学
内容:用 2D 定向高斯盘来替代传统的 3D 高斯体元把场景体积“折叠”为一系列贴表面的 2D 高斯元,高斯参数保留切向向量和scale,易于计算法线
3DGS-Enhancer: Enhancing Unbounded 3D Gaussian Splatting with View-consistent 2D Diffusion Priors
会议:NeurIPS 2024
作者:Xi Liu, Chaoyi Zhou, Siyu Huang
单位:Clemson University
内容:利用 Stable Video Diffusion 模型生成视图一致的图像先验,将 2D 扩散结果蒸馏回 3DGS,显著改善无界场景一致性与视觉质量。
Gaussian Splatting with Discretized SDF for Relightable Assets
会议:ICCV 2025
作者:Zuo-Liang Zhu、Jian Yang、Beibei Wang
单位:南开大学/南京大学
内容:用2DGS得到法线,将Discretized SDF引入到 3DGS表示中
Mip‑Splatting: Alias‑free 3D Gaussian Splatting
会议:CVPR 2024
作者:Zehao Yu, Anpei Chen, Binbin Huang, Torsten Sattler, Andreas Geiger
内容:在 拍摄距离/焦距变化(采样率变化)下产生锯齿/混叠 (aliasing) 的问题:提出一个 3D 平滑滤波器 + 2D Mip 滤波器
EDGS: Eliminating Densification for Efficient Convergence of 3DGS
会议:
作者:Dmytro Kotovenko,Olga Grebenkova,Björn Ommer
单位: Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU Munich)
内容:根据roma在train之前计算稠密点,通过获得的置信度图片和点对,修改三角化过程,在训练过程中跳过致密化环节
使用RoMa 网络 输入两幅图像,输出像素对应图 以及置信度图片
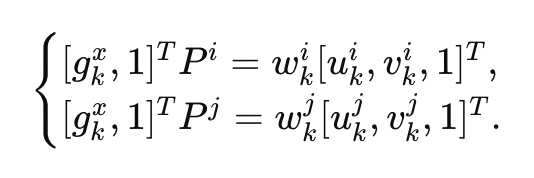
gkx 三维空间中某个点 经过 相机投影矩阵P(3*4)投射到对应像素位置 (u,v) w归一化
3行除以1行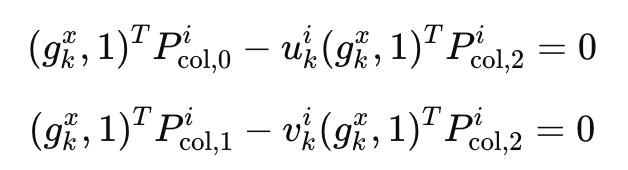
四条公式的约束: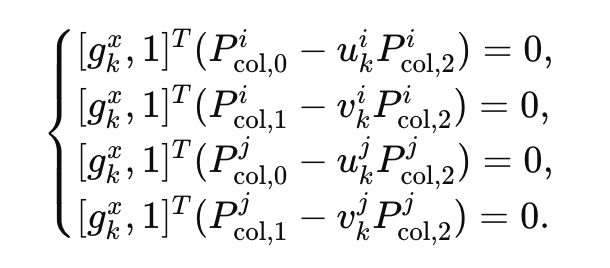
类似 opencv triangulatePoints()过程
4D Gaussian Splatting: Modeling Dynamic Scenes with Native 4D Representation
作者:
会议:ICLR2024
单位:复旦大学
动态场景的4D高斯模型
引入每个时间 高斯对像素影像的概率p(u,v|t)
pi(t)p_i(t)pi(t):第 iii 个高斯在时间 t 存在或起作用的总体概率(比如这个高斯在 t 时刻是否还“存在”);
pi(u,v∣t)p_i(u,v|t)pi(u,v∣t):在时间 t 时,它在屏幕坐标 (u,v) 上的条件投影概率(它在屏幕上投到哪儿)。
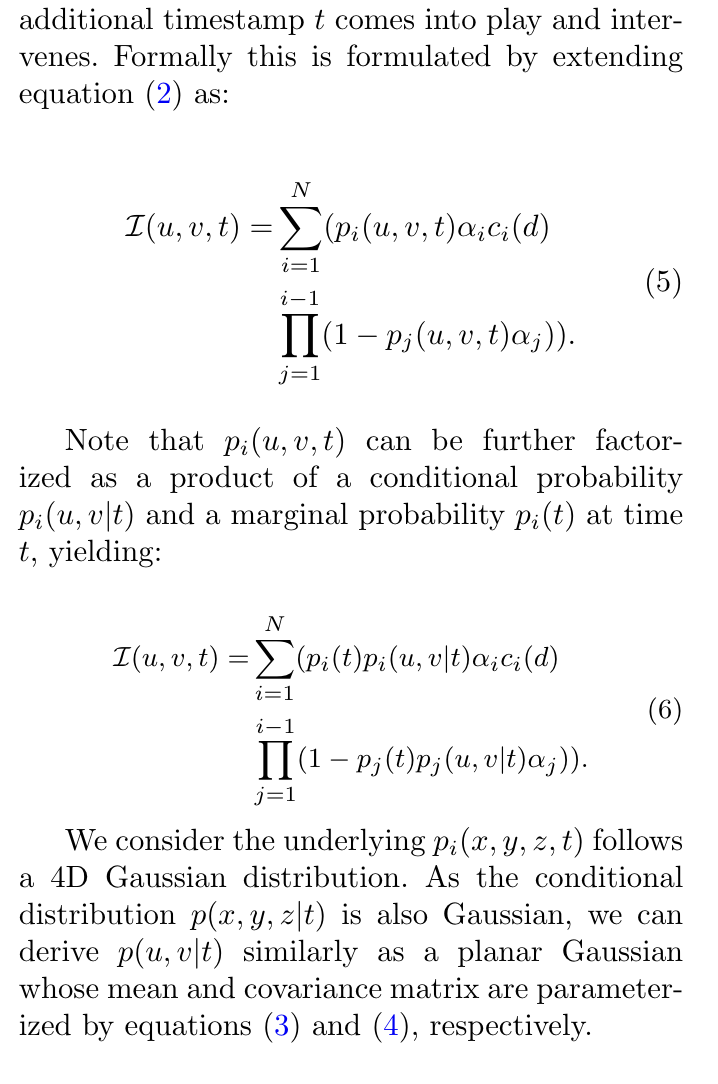
把时间t融入到高斯球属性,均值属性,求解协方差矩阵时也求解4x4的矩阵
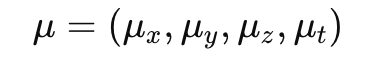
SDD-4DGS: Static-Dynamic Aware Decoupling in Gaussian Splatting for 4D Scene Reconstruction
4D Gaussian Videos with Motion Layering
存储初始高斯以及每帧位移 不存储高斯颜色旋转尺度等变化
Sc-gs: Sparsecontrolled gaussian splatting for editable dynamic scene
用控制点 + LBS
4D3R:motion-aware neural reconstruction and rendering of dynamic scences from monocular videos
在sc-gs基础上 去除了colmap
项目总结
1.收获:思路方面更加严谨,发现问题解决问题的思路,比如输出深度图,用可视化方式去看每一次迭代的图像变化等等。虽然麻烦但是能发现问题所在
2.在论文撰写方面,熟悉投稿流程和overleaf等等,在形式上发一篇论文没问题
3.对3DGS源码的了解,
思考
1.项目管理问题,版本非常多,现在用V1-V22版本,每个版本上又有不同的变种和参数,调试起来困难难对齐
2.一直在尝试不同trick并没能确定一个最终版本去调试参数,最终很多调试其实并没有用上,比如正则化能提高PSNR但是增加了时间,剪枝在train场景效果很好但在其他场景一般而且稀释了active set的效果
3.我在测试之后没有出具好读的文档,都是通过问的方式确定参数,有些参数就很难对齐
尝试了在长轴生成点/用taming的fps做剪枝视角选择/每次训练都记录所有高斯点的vi/
项目数据
| 各步骤时间 | 无加速 | k=30 | k=50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| backward_time | 71.37 | 46.26 | \ |
| densification | 0.3764 | \ | \ |
| forward_time | 75.4 | 58.25 | \ |
| step | 93.51 | 55.15 | \ |
| active_update | 0 | 49.7 | 80.34 |
| total_time | 250.4 | 219.5 | 254.1 |
| PSNR | 22.28 | 21.40 | 21.46 |
无排序无截断:231.39229482913035 前15000次
有排序有截断:289.9748523981556 前15000次
active_update各步骤时间(单视角单迭代)
| step | time(ms) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| render | 3.459 | 7.277 | 2.773 |
| loss computation | 0.805 | 0.772 | 0.577 |
| backward | 5.652 | 5.312 | 4.332 |
| add_gradient_stats | 1.209 | 1.710 | 1.055 |
| optimizer.zero_grad | 0.237 | 0.405 | 0.218 |
| total | 11.362 | 15.475 | 8.955 |
| opacity | PSNR |
|---|---|
| 0.0005 | 21.435432936015882 |
| 0.005 | base |
| 0.05 | 21.438090826335706 |
| 0.5 | 21.491223259976035 |
| vi_lr | PSNR |
|---|---|
| 0.0005 | 21.220848961880332 |
| 0.005 | base |
| 0.05 | 21.346949602428236 |
| 点数 | |
| 第15100次 | |
| total_number = 796604 | |
| Inactive points - New: 784918 ratio: 0.9853 |
第15200次
total_number = 796604
Inactive points - New: 697601 ratio: 0.8757
Inactive points - Added: 911 and ratio: 0.0013
Inactive points - Removed: 88228 and ratio: 0.1265
第15300次
total_number = 796604
Inactive points - New: 697064 ratio: 0.8750
Inactive points - Added: 10581 and ratio: 0.0152
Inactive points - Removed: 11118 and ratio: 0.0159
第15400次
total_number = 796604
Inactive points - New: 696749 ratio: 0.8746
Inactive points - Added: 8286 and ratio: 0.0119
Inactive points - Removed: 8601 and ratio: 0.0123
最后稳定在add和remove 4000左右
xyz_grad_threshold = 1e-3
scaling_grad_threshold = 1e-6
rotation_grad_threshold = 1e-5
opacity_grad_threshold = 1e-6
weight_v_grad_threshold = 1e-5
feature_grad_threshold = 5e-6
19.74828004837036
22.37305570903577
| step1 | 3.771 |
| step2 | 4.075 |
| step3 | 13.81 |
| step4 | 3.245 |
| step5 | 41.05 |
| step6 | 3.421 |
| gradient | k | PSNR | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 22.147510277597526 |
RP
三维资产重建
三维场表示方式 3DGS
FlipNeRF [55] and MixNeRF [ 56 ]. FlipNeRF signifi-
cantly reduces floating artifacts by introducing flipped reflective rays to filter out invalid
light rays and accurately reconstruct surface normals.
SuGaR utilizes surface-aligned
Gaussian distributions to accurately extract meshes and quickly and scalably generate
meshes using a Poisson reconstruction algorithm. Additionally, SuGaR introduces an op-
tional refinement strategy, enhancing mesh quality and rendering effects through Gaussian
binding and joint optimization. This method not only improves reconstruction accuracy but
also facilitates subsequent applications such as editing, sculpting, animation, and relighting.
PixelSplat
In addition, in terms of 3D editing, the introduction of PixelSplat [ 88] technology
provides users with a more flexible and efficient 3D creation tool. This technology leverages
a feedforward model to reconstruct a 3D radiance field parameterized by 3D Gaussian
primitives from input image pairs, achieving scalable training and fast 3D reconstruction.
At the same time, the generated 3D radiation field is interpretable and editable, providing
users with rich creative materials and convenient means of creation in multiple fields such
as VR/AR, game development, and architectural design. The emergence of PixelSplat
technology has further promoted the development of 3D editing technology, bringing users
a richer creative experience and a broader creative space.
Our method
consists of a two-view image encoder and a pixel-aligned
Gaussian prediction module
通过明暗场学习高斯法线参数
3DGS可编辑 可以调材质/纹理/光照
目前可能可以获取的先验信息,扫一次物体得到的图像uncertianly热力图,然后能够进行NBV,重新获取该视角下的物体图片。






